Geoffrey Moore introduced the technology sector to the Technology Adoption Life-Cycle (1). He documented the stages every product or service goes through. He explained how growth varies at each stage. It’s slow during the early adopter phase, speeds up during the early majority then slows and declines in the late majority and laggard phases.
Vendors with all of their products in the early majority phase don’t have an immediate problem with growth. For everyone else, growth presents a challenge. Outcome-based vendors understand the Technology Adoption Lifecycle applies to them. So, they constantly plan for new sources of growth. And they use a new lens to plan that growth – the success outcome they serve.
There are two types of customer outcomes.
– the direct benefit of using your products or services
Success outcomes
– what the customer really wants to achieve; what the customer considers to be success
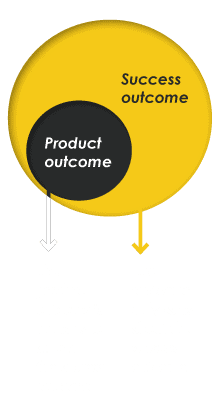
Success Outcomes create a new To-Be state and have an emotional connection for the customer.
To illustrate…
Step 1 – Why Outcomes?
Help key people in your business understand why they should adopt an outcome-based approach to engaging with customers.
| Vendor Type | Product Outcome | Success Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| ERP | Automated processes, planning and reporting |
Effective operations, lower costs |
| Marketing Automation | Well-executed campaigns | Pipeline of a certain value |
| Content Management | Information available | Good decisions |
BEND Growth Model
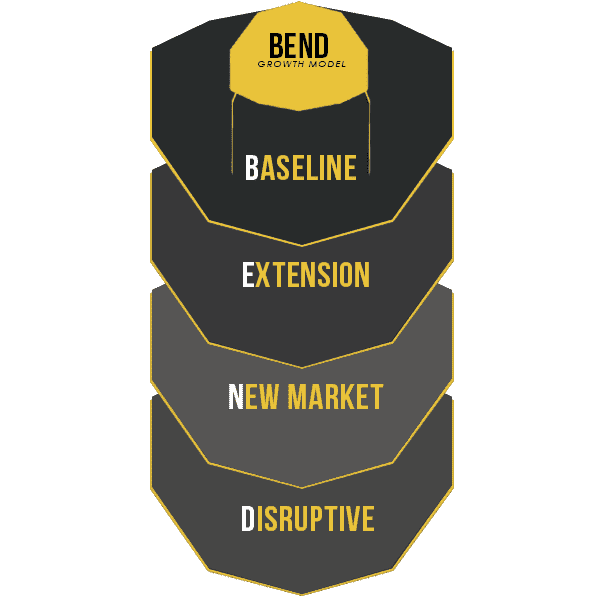
The four types form a somewhat fortuitous acronym – BEND. It’s fortuitous as vendors need a flexible growth planning framework. The industry changes quickly. Vendors need a growth planning process that can adapt or bend to suit the changing environment.
Outcome-based growth planning uses four different types of growth –
• Baseline
• Extension
• New-Market
• Disruptive
Choosing What to Do.
Outcome-based vendors plan for growth regularly. They create lots of innovative ideas. They’ll almost always have too many ideas to implement them all. The next step is to sort and prioritise the ideas then generate a practical action plan.
Outcome-based Customer Success uses a concept called Capability Circles to sort then prioritise the ideas. You’ll then build a practical plan to execute the ideas you’ve chosen.
“Crossing the Chasm; Moore, Geoffrey A. 1991 Harper Business”
Step 4 – Execution Planning
In this step, we’ll help you plan the staged rollout of Outcome-based Customer Success. We recommend beginning with a pilot program and will help you build a practical approach for your pilot.
The level of assistance we provide after setting up the pilot will be up to you. You may feel you can proceed without further assistance.
The price for this stage will vary depending on the level of help you’d like from us.
Step 5 – Staged Roll Out
Launch your Stage 1 Plan to Customers, Staff and Partners.

The lens of success outcomes helps you see great new growth opportunities. For example,
Doing More of What the Customer Needs to Achieve their Success Outcome
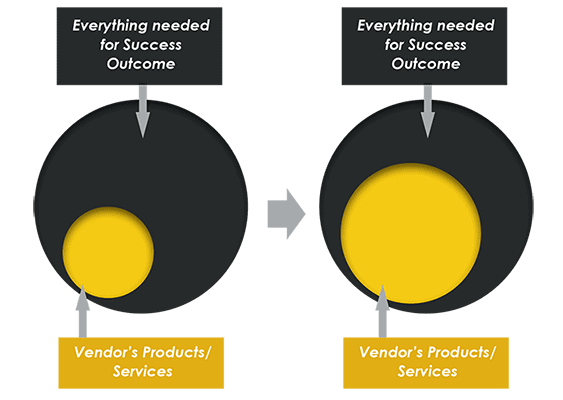
You can grow revenue by expanding the range of products and services you offer to enable the success outcome.
You can displace other vendors or do things the customer currently has to do themselves.
There are four types of Generation 3 Growth




